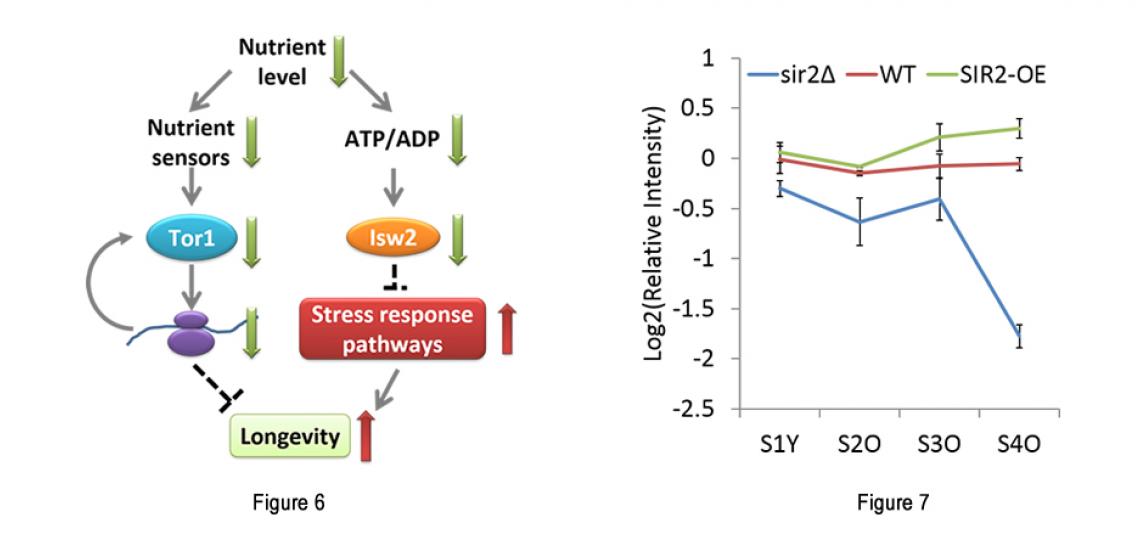
Replicative Aging of Budding Yeast
Stem cell aging and cellular senescence are important processes that contribute to the aging pathology and development of cancer. As a complement to our yeast replicative aging model, we are using mammalian primary cell lines and adult stem cells to study whether and how chromatin and epigenetic regulation pathways identified in yeast are involved in stem cell aging and cellular senescence. Changes in aging and senescence phenotype are investigated by knocking down conserved enzymes. Epigenetic features are tracked during senescence and compared between young and old stem cells.
Studying mechanistic conservation using mammalian cell models will provide valuable insights into mammalian aging and conditions predisposed to cancer development.
Epigenetics
Epigenetics generally includes all cellular alterations beyond genetic changes that result in observable phenotypes. In practice, epigenetics usually means persistent covalent alterations to chromatin, such as histone acetylation and DNA methylation. Recent proteomics and acetylomics studies have broadened our views of epigenetics and many more enzymes and factors can carry modifications that confer epigenetic phenomena. It is very clear now epigenetics represents a complex regulation network on top of the genetic code. In medicine, epigenetics holds a very promising future because interventions in epigenetics can alter genetic outcomes and the strength of such intervention can be fine-tuned.

Stem Cell Aging and Cellular Senescence
Stem cell aging and cellular senescence are important processes that contribute to the aging pathology and development of cancer. As a complement to our yeast replicative aging model, we are using mammalian primary cell lines and adult stem cells to study whether and how chromatin and epigenetic regulation pathways identified in yeast are involved in stem cell aging and cellular senescence. Changes in aging and senescence phenotype are investigated by knocking down conserved enzymes. Epigenetic features are tracked during senescence and compared between young and old stem cells. Studying mechanistic conservation using mammalian cell models will provide valuable insights into mammalian aging and conditions predisposed to cancer development.