Gout
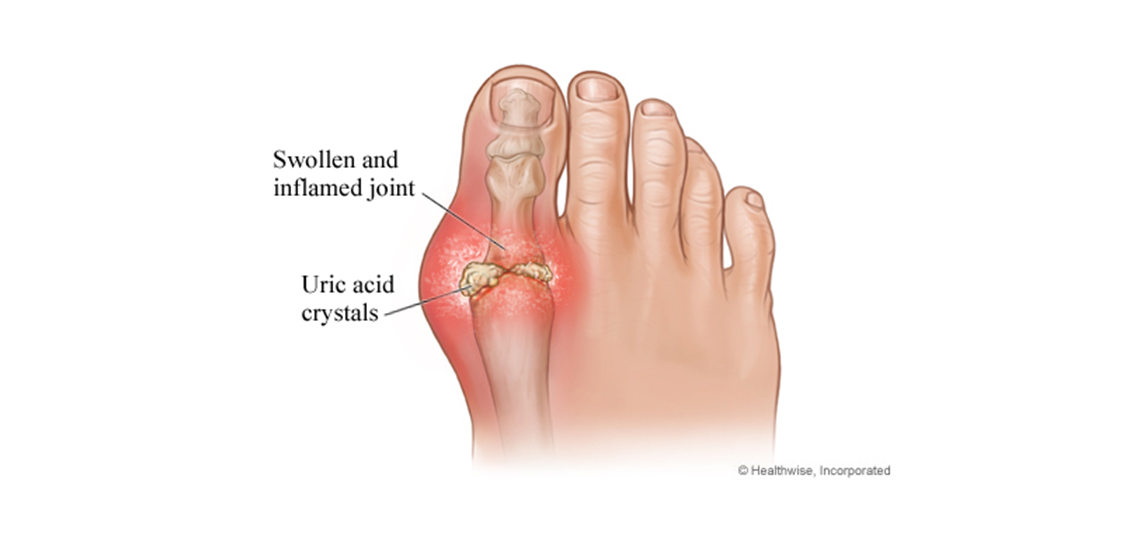
Gout is a form of arthritis caused by a buildup of uric acid crystals in a joint. It causes sudden attacks of pain, swelling, redness, and stiffness, usually in one joint, especially the big toe.
Gout usually comes on without a cause. But it can be brought on by drinking alcohol (especially beer) or eating seafood and red meat. Taking certain medicines, such as diuretics or aspirin, also can bring on an attack of gout.
What Causes Gout?
Gout is caused by too much uric acid in the blood (hyperuricemia). Most of the time, having too much uric acid isn't harmful. Many people with high levels in their blood never get gout. But sometimes when uric acid levels in your blood are too high, the uric acid forms hard crystals that build up in your joints. This causes pain and other symptoms.
In some cases, the exact cause isn't known. But inherited factors (genes) seem to play a role.
Gout can seem to flare up without specific cause. Or it can be brought on by:
- Certain conditions, such as being overweight, eating a diet rich in meat and seafood (high-purine foods), and drinking too much alcohol.
- Medicines that may increase uric acid concentration, such as regular use of aspirin or niacin or using medicines that reduce the amount of salt and water in the body (diuretics).
- Major illness or certain medical conditions, such as rapid weight loss or high blood pressure.
- Surgery.
- Having been born with a rare condition that causes high blood uric acid levels. People with Kelley-Seegmiller syndrome or Lesch-Nyhan syndrome may lack an enzyme that helps control uric acid levels.
Pseudogout
Pseudogout is a type of arthritis that causes pain, redness, heat, and swelling in many joints, symptoms that resemble those of gout. Unlike gout, though, the symptoms of pseudogout are caused by deposits of tiny crystals of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate rather than uric acid.
In pseudogout, the joint-most often affected is the knee. Over time, pseudogout may damage the cartilage of the joint. As this happens, the bones rub together and cause joint pain. Pseudogout usually affects people in their 60s and is rarely seen in people younger than 30.
© 2016-2020 Healthwise, Incorporated








 Credit
Credit