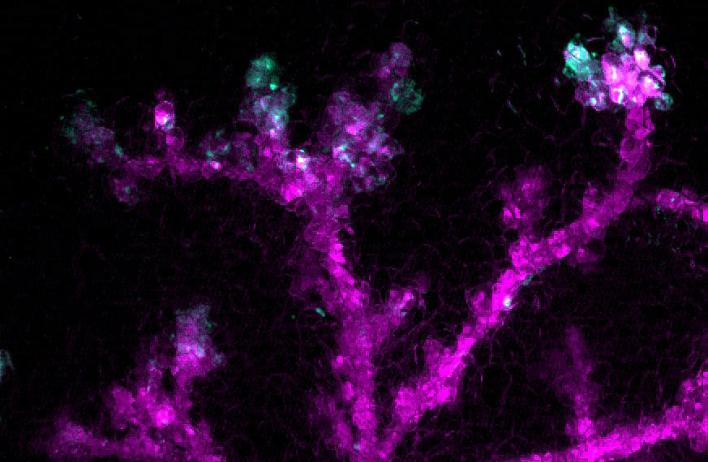
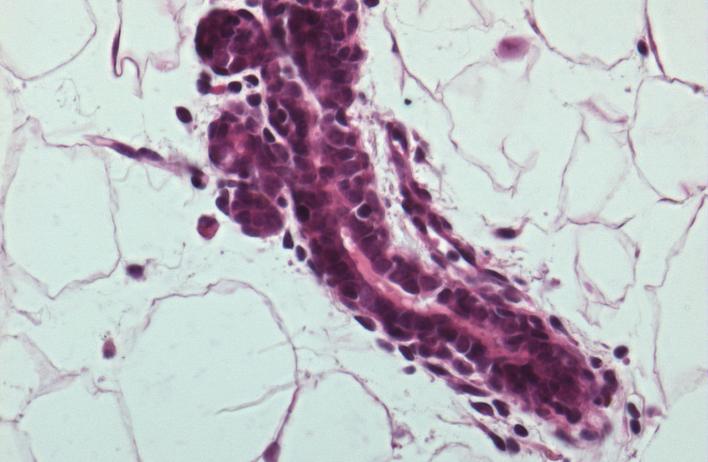
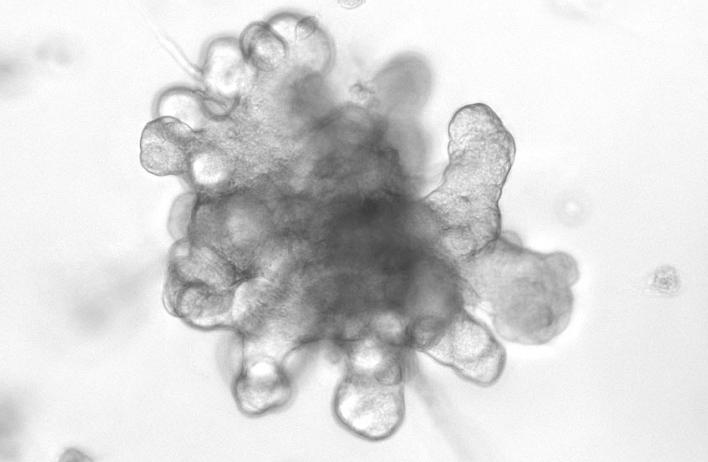
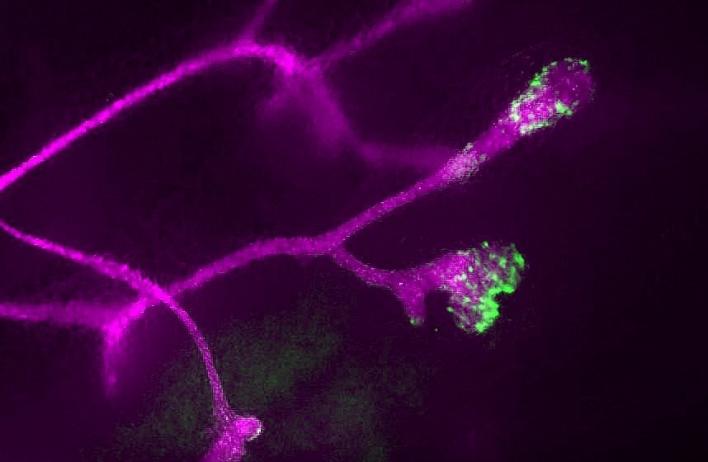
The canonical Wnt/beta-catenin pathway is the best understood arm of the Wnt pathway, mediated by the stabilization of beta-catenin within the cell, where it can function as a transcriptional co-activator with Tcf/Lef family members in the nucleus. Several lines of evidence suggest this pathway regulates mammary stem cell dynamics in normal mammary epithelial homeostasis.
We are particularly interested in how alternative “noncanonical” modes of Wnt signaling, which are beta-catenin independent, are integrated with canonical Wnt signaling in epithelial subsets of the gland in order to shape:
- Wnt signaling specificity in vivo
- Coordination of cellular collectives responsible for appropriate mammary epithelial development.
Ongoing research in the lab is focused on illuminating novel functions for Wnt signaling in directing complex spatial and temporal cues necessary for appropriate mammary epithelial homeostasis.