Project Co-leaders
- Xi Chen, Ph.D. (Basic Science Leader)
- Mothaffar Fahed Rimawi, M.D. (Clinical Science Leader)
- Xiang Zhang, Ph.D. (Basic Science Leader)
Project Description
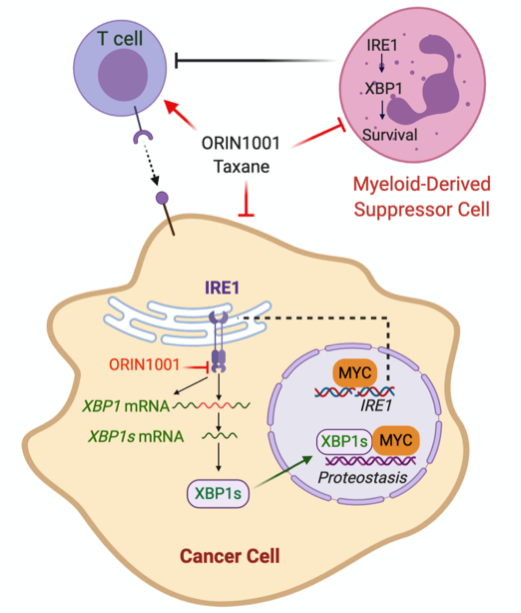
Limited sensitivity to chemotherapy and an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment drives breast cancer mortality in HER2 negative breast cancer. We have identified the IRE1/XBP1 branch of the Unfolded Protein Response (UPR) or endoplasmic reticulum (EnR) stress response as a previously unexplored therapeutic vulnerability in MYC-driven breast cancer that enhances chemotherapy sensitivity and reverses the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. I
RE1 is amplified in ~10 percent of human breast cancer, and frequently co-amplified with the MYC oncogene. Activation of MYC is synthetic lethal with IRE1/XBP1 pathway inhibition. We found that inhibition of the IRE1/XBP1 pathway with a highly selective IRE1 RNase inhibitor ORIN1001 suppresses MYC-high-expressing (MYChigh), but not MYC-low-expressing (MYClow), tumor growth in patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models. ORIN1001 substantially enhances the docetaxel efficacy, resulting in rapid tumor regression of the MYChigh PDX tumors. Furthermore, the ORIN1001 plus docetaxel therapy triggers massive cytotoxic T-cell infiltration, depletion of immunosuppressive myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and substantial upregulation of PD-L1 in the tumor microenvironment. ORIN1001 has excellent safety profile and is well-tolerated.
These preclinical data prompt us to hypothesize that inhibition of the IRE1/XBP1 pathway with the IRE1 inhibitor ORIN1001 compromises MYChigh breast cancers by inhibiting obligatory UPR stress adaptation required for cellular viability. This therapeutic effect of ORIN1001 is associated with a marked increase in taxane sensitivity. In addition, MDSCs are also selectively depleted by ORIN1001 in the presence of a taxane, thus reversing immunosuppression and potentially sensitizing MYChigh breast cancers to immune checkpoint intervention. A pre-clinical phase study in breast cancer models will be conducted in parallel with a Phase 1 clinical trial.
The overarching objective of this proposal is to design and open a Phase 2 clinical trial in MYC-positive metastatic breast cancer with eligibility and endpoints to be defined by the execution of the research aims.








