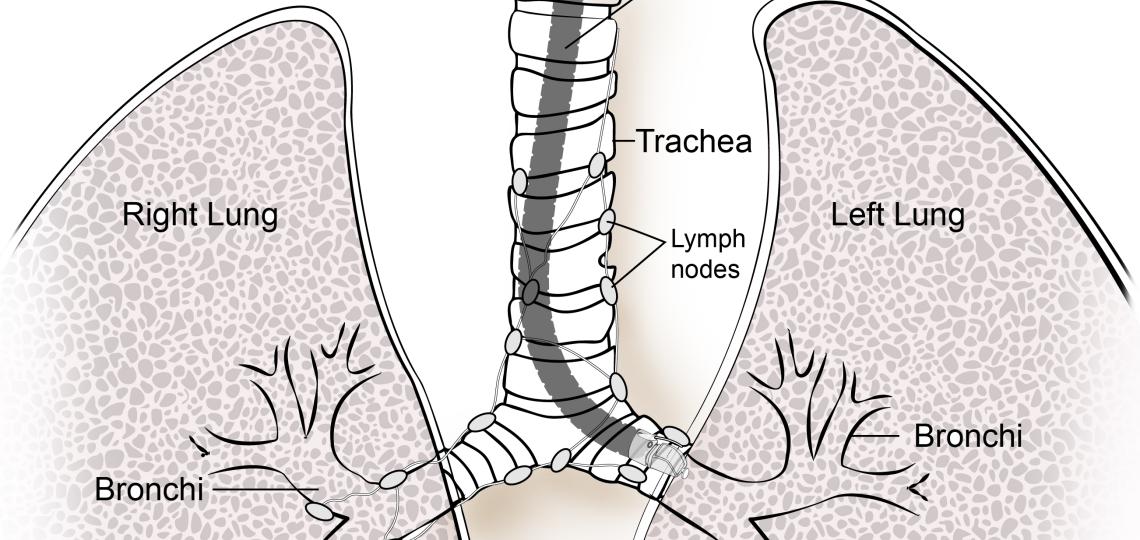
Endobronchial Ultrasound (EBUS) is a minimally invasive procedure used to diagnose and treat diseases of the airways. During an EBUS, a small ultrasound probe is inserted through the mouth and into the airways. The probe is used to take images of the inside of the airways, which can help diagnose and treat certain conditions, such as lung cancer.
Endobronchial Ultrasound is used to diagnose and treat certain diseases of the airways, such as lung cancer. It can also be used to diagnose and treat other conditions, such as pneumonia, bronchiectasis, and COPD.
Endobronchial Ultrasound is typically recommended for people with suspected lung cancer or other conditions of the airways. It can also be used to diagnose and treat other conditions, such as pneumonia, bronchiectasis, and COPD.
Recovery
After an EBUS procedure, most people can go home the same day and resume their normal activities. The procedure is relatively safe, with few side effects. In some cases, patients may experience some soreness in the throat, but this should subside within a few days. Overall, Endobronchial Ultrasound is a safe and effective way to diagnose and treat certain diseases of the airways.








 Credit
Credit