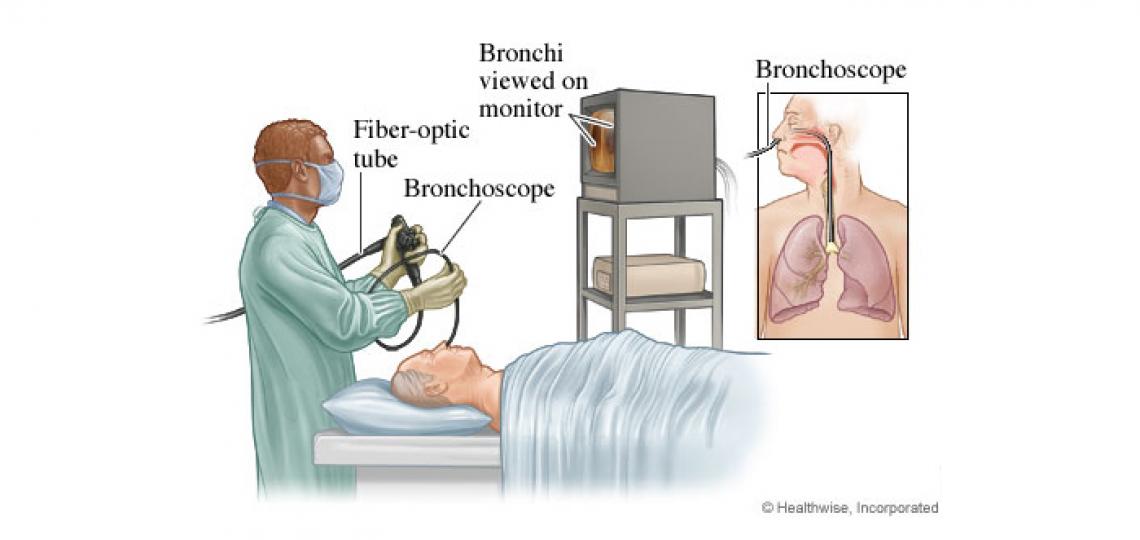
A bronchoscopy is performed with a small flexible tube (bronchoscope). The scope is inserted through your nose or mouth and will be used to look at your airway. This is typically performed when you are asleep at the beginning of a thoracic surgery operation to evaluate the anatomy of the airway, and to assist in the staging of thoracic cancers.
Robotic Navigational Bronchoscopy
Robotic navigational bronchoscopy is an advanced minimally invasive procedure that allows physicians to visualize and access the lungs more effectively than traditional bronchoscopy. It offers patients a less invasive option for lung examination and treatment, with the potential for improved outcomes and reduced recovery times compared to traditional methods.
- Preparation: Before the procedure, patients may undergo imaging tests such as CT scans to determine the best approach for navigating to the targeted area in the lungs. Patients are usually advised to fast for several hours prior to the procedure.
- Anesthesia: The procedure typically requires sedation or general anesthesia to ensure the patient is comfortable and relaxed. An anesthesiologist will monitor the patient's vital signs throughout the process.
- Procedure: Once sedated, a thin, flexible tube called a bronchoscope is inserted through the mouth or nose and into the airways. With robotic assistance, the bronchoscope can be maneuvered with greater precision, allowing the physician to navigate complex airway structures. The robotic system provides 3D visualization to enhance accuracy.
- Biopsy or Treatment: If necessary, the bronchoscopy can be used to take biopsies of lung tissue or to deliver treatments, such as medications directly into the lungs. The robotic system allows for better targeting of lesions that may be difficult to reach using conventional methods. To target these lesions, a fiducial or marker may be placed inside the lungs to help the team locate a lesion more easily.
- Recovery: After the procedure, patients are monitored as the sedation wears off. They may experience some throat discomfort or coughing but are generally able to return home the same day. It’s important for patients to follow post-procedural instructions, including any restrictions on activities.
- Follow-Up: Patients will have follow-up appointments to discuss results and any further treatment options if needed. The robotic navigational bronchoscopy can provide critical information for diagnosing and managing lung conditions.
A robotic navigational lung bronchoscopy may be combined with an endobronchial ultrasound.








 Credit
Credit