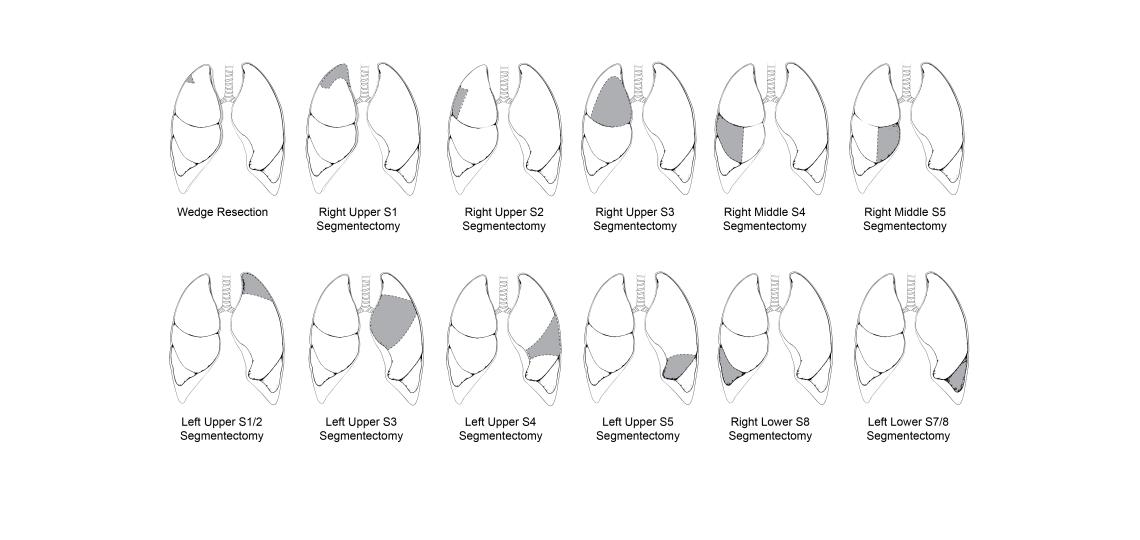
A segmentectomy is a surgical procedure that removes one of the ten anatomic segments of a lung. It requires some dissection of the artery, vein, and/or airway structures of that segment, and the segment is removed along its anatomic boundaries.
Both segmentectomy and wedge resection procedures are usually performed when a small cancer is found in a small area of the lung.
A wedge resection is like a segmentectomy, but it is typically a smaller resection and does not require the dissection of vascular or airway structures. A wedge resection is performed to remove the cancerous cells along with a margin of healthy tissue surrounding the area.
Procedure
During a lung segmentectomy or wedge resection, a surgeon will make small incisions on the chest and use minimally invasive instruments to remove a segment or wedge of the lung. Some lymph nodes are typically removed when the operation is done for a cancer. The incisions are closed with sutures and a drainage tube is typically left in for one night.
Recovery
After the surgery, patients will typically spend 1-2 days in the hospital for monitoring. Pain and discomfort are common after the procedure and are managed with medications. Most patients can return to normal activities within a few weeks, but the exact recovery time will depend on the individual. It is important to follow the surgeon's instructions for proper recovery.








