Peripheral Arterial Disease
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is a narrowing or blockage of arteries that causes poor blood flow to your legs or arms.
The most common cause of PAD is the buildup of plaque in blood vessels called "hardening" of the arteries. If you have hardening of the arteries in your legs, you most likely will have it in the arteries of your heart and brain. This increases your chance of having a heart attack or stroke.
Treatment for PAD includes ways to lower your risk of heart attack and stroke.
How is surgery used to treat peripheral arterial disease (PAD) of the legs?
Most of the time, surgery is only done in cases of severe PAD. These are cases that involve intermittent claudication; open sores; or serious skin, bone, and tissue problems (gangrene).
Bypass surgery redirects blood through a grafted blood vessel. This bypasses the blood vessel that is damaged.
The type of surgery used to treat PAD will depend on the size and location of the affected leg artery or arteries. Surgeries include:
Aortobifemoral bypass.Femoropopliteal (fem-pop) bypass..Femoral-tibial bypass.Endarterectomy. This is not done as often as other surgeries for PAD. It is most often done on the large femoral artery. This artery is in your groin and upper thigh area.
Angioplasty
Angioplasty is a procedure for severe PAD that causes pain and limping during exercise, pain when at rest, or open sores.
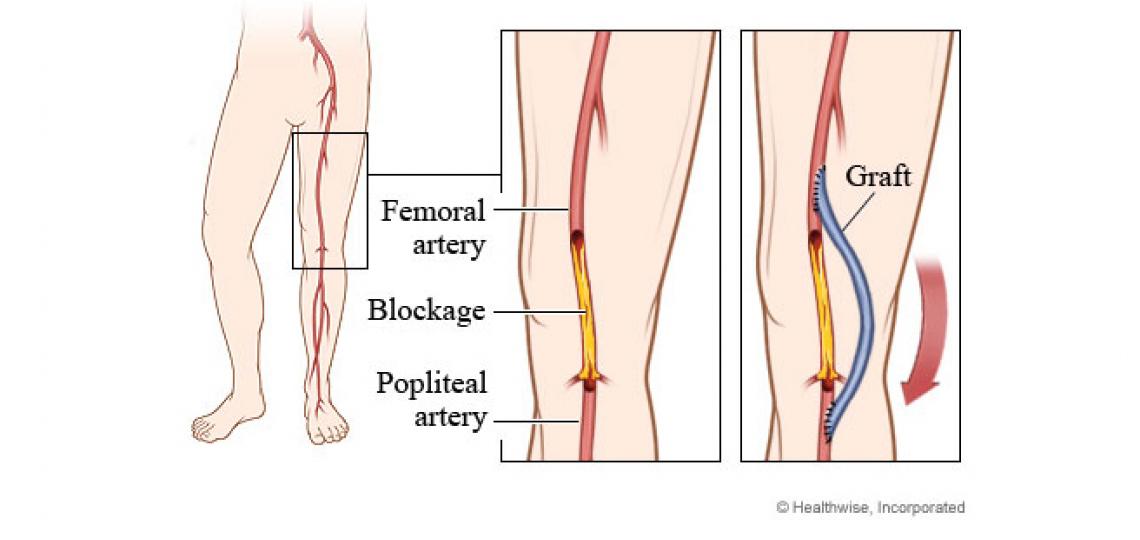
Femoropopliteal bypass (fem-pop bypass)
Femoropopliteal (fem-pop) bypass surgery is used to bypass diseased blood vessels above or below the knee.
To bypass the narrowed or blocked blood vessel, blood is redirected through either a healthy blood vessel that has been transplanted or a man-made graft material. This vessel or graft is sewn above and below the diseased artery so that blood flows through the new vessel or graft.
Before you have surgery, the doctor will determine what type of material is best suited to bypass the blood vessel. Whenever possible, the surgeon will choose to use an existing piece of vein taken from the same leg. Man-made graft materials (such as polytetrafluoroethylene [PTFE] or Dacron) are more likely to become narrowed again, but they are still effective.
The section of vein or man-made blood vessel graft is sewn onto both the femoral and popliteal arteries so that blood can travel through the new graft vessel and around the narrowed or blocked area.
General anesthesia or an injection in the spine (epidural) is used for this surgery. General anesthesia will cause you to sleep through the procedure. An epidural prevents pain in the lower part of the body.
What can you expect after femoropopliteal bypass (fem-pop bypass) for peripheral arterial disease?
You may stay in the hospital 2 to 4 days after surgery. You can likely begin sitting up and walking the first day after surgery.
You will have some pain from the cuts (incisions) the doctor made. This usually gets better after about 1 week. You can expect your leg to be swollen at first. This is a normal part of recovery and may last 2 to 3 months.
You will need to take it easy for at least 2 to 6 weeks at home. It may take 6 to 12 weeks to fully recover.
You will probably need to take at least 2 to 6 weeks off from work. It depends on the type of work you do and how you feel.
You will need to have regular checkups with your doctor to make sure the graft is working.
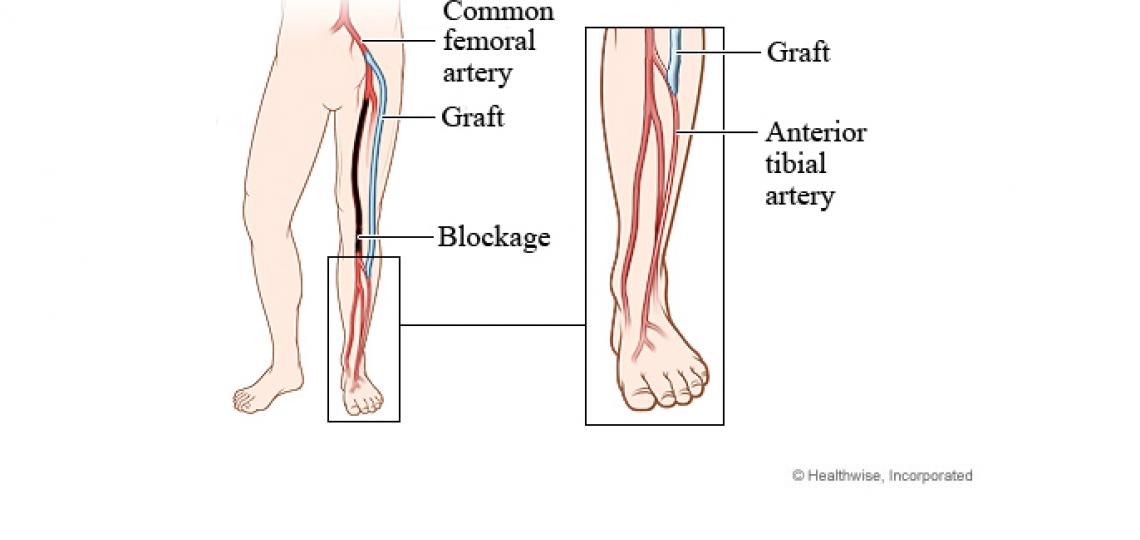
What is a femoral-tibial bypass?
Femoral-tibial bypass is surgery to bypass diseased blood vessels in the lower leg or foot. The surgery is most often done to help with severe pain or help heal foot sores caused by bad blood circulation.
Your doctor uses a graft to bypass the blocked area of the blood vessel. The graft is most often a vein taken from another place in your leg. Sometimes the graft is a man-made blood vessel. The graft will carry blood from the femoral artery in your groin to the tibial artery in your lower leg or foot.
This surgery is also known as infra-popliteal reconstruction.
What to Expect at Home—Your Recovery
Femoral-tibial bypass is surgery to bypass diseased blood vessels in the lower leg or foot.
You will have some pain from the cuts (incisions) the doctor made. The pain usually gets better after about 1 week. Your doctor will give you pain medicine. You can expect your leg to be swollen at first. This is a normal part of recovery and may last 2 or 3 months.
You may need to stay in the hospital for 3 to 5 days.
You will need to take it easy for 2 to 6 weeks at home. It may take 6 to 12 weeks to fully recover.
You will need to have regular checkups with your doctor to make sure the graft is working.
© 2016-2019 Healthwise, Incorporated.
Patient Information
Clinical trials, terminology and frequently asked questions about vascular surgery.








 Credit
Credit