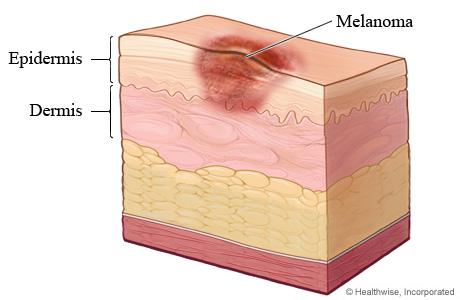
What is Melanoma?
Melanoma is the most serious kind of skin cancer. Most melanomas show up as a new spot or skin growth. But they can also form in an existing mole. Melanoma can affect your skin only, or it may spread to your organs and bones.
What Causes Melanoma?
Too much UV radiation from sun exposure causes normal skin cells to become abnormal. These abnormal cells quickly grow out of control and attack the tissues around them.
You can get melanoma by spending too much time in the sun. You are at higher risk for melanoma if you have any of these:
- Fair skin
- A family history of melanoma
- Many abnormal, or atypical, moles. These moles may fade into the skin and have a flat part that is level with the skin. They may be smooth or slightly scaly. Or they may look rough and "pebbly."
What are the Symptoms of Melanoma?
You may not have any symptoms in the early stages of melanoma. Or a melanoma may be sore, or it may itch or bleed.
Melanoma usually starts as a new skin growth. But it can develop in an existing mole or other mark. Melanomas can grow anywhere on the body.
The most important warning sign of melanoma is any change in size, shape, or color of a mole or other skin growth. The ABCDE system tells you what to look for.
- A for asymmetry. One half of the mole doesn't match the other half.
- B for border irregularity. The edges are ragged, notched, or blurred.
- C for color. The color isn't the same throughout the mole.
- D for diameter. The mole is larger than the size of a pencil eraser.
- E for evolution. There's a change in the size, shape, symptoms (such as itching), surface (especially bleeding), or color of a mole.
How is Melanoma Diagnosed?
To check for melanoma, your doctor may:
- Do a physical exam of your skin. Your doctor will check your skin to look for melanoma.
- Do a skin biopsy. Your doctor will take a sample of your skin and have it tested for melanoma.
- Check your lymph nodes to see if they are larger than normal. This may be followed by a sentinel lymph node biopsy to see if the melanoma has spread to your lymph system.
- Do imaging tests. These tests include PET scan, CT scan, and MRI. These tests can show if the cancer has spread to other parts of your body, such as the lungs, brain, or liver.
Other techniques may include total-body photography. A series of photos of the suspicious lesions may be taken. These photos can be used as a baseline to compare with follow-up photos.
Where Does Melanoma Usually Spread?
Melanoma usually spreads (metastasizes) first into nearby lymph nodes. It can also spread through the bloodstream. Distant metastases typically are found in the skin, liver, lungs, bone, and brain.
How is Melanoma Treated?
Treatment for melanoma is based on the stage of the cancer and other things, such as your overall health. The main treatment is:
- Surgery: The doctor removes the melanoma and a border of normal tissue. In some cases, the doctor may remove the first lymph node that the cancer may have spread to. If cancer is found, nearby lymph nodes may be removed and checked for cancer.
Other treatments may include:
- Immunotherapy: This treatment helps your immune system fight cancer.
- Targeted therapy: These medicines attack only cancer cells, not normal cells. They help keep cancer from growing or spreading.
- Chemotherapy: These medicines kill fast-growing cells, including cancer cells and some normal cells.
If melanoma has spread (metastatic cancer), surgery may be done. You’ll probably need other treatments too. Sometimes a clinical trial may be a good choice.
Your doctor will talk with you about your options and then make a treatment plan.
© 2016-2020 Healthwise, Incorporated.








 Credit
Credit